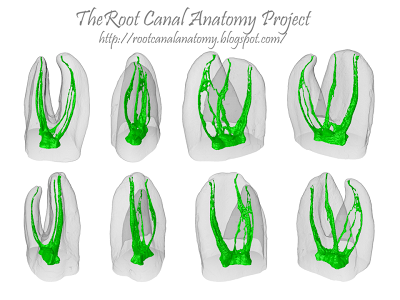
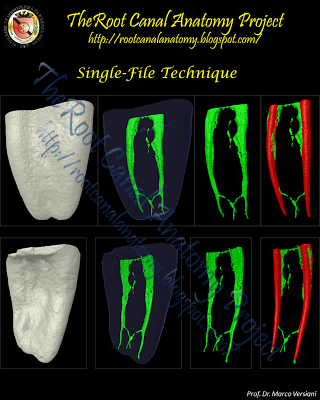
Cover: 3-D micro-CT models of a mandibular molar showing the changes of the original root-canal anatomy (green) after preparation with a multiple-file rotary system. Each color represents preparation by one of five instruments. The last image in the sequence represents the root canal after shaping (red) superimposed on the original canal (green), demonstrating that most of the surface area was prepared using the multiple-file system.
Click on the picture to enlarge
Thanks to Oemus (in the name of Magda Wojtkiewicz) for the invitation to write the Editorial of this issue of Roots magazine as well as to illustrate the cover. I hope you also enjoy it!
Best regards,
Prof. Dr. Marco Versiani