From 2011-2016, images and videos of "The Root Canal Anatomy Project" were developed at the Laboratory of Endodontics of Ribeirao Preto Dental School. From 2016, images were acquired in other educational institutions. They can be freely used for attributed noncommercial educational purposes by educators, scholars, student and clinicians. It means that all material used should include proper attribution and citation (http://rootcanalanatomy.blogspot.com). In such cases, this information should be linked to the image in a manner compatible with such instructional objectives. Unfortunately, because material shared on the RCAP has not been properly cited by several users, from November 2019 a watermark was added to the images and videos. Enjoy!
May 25, 2014
May 24, 2014
May 19, 2014
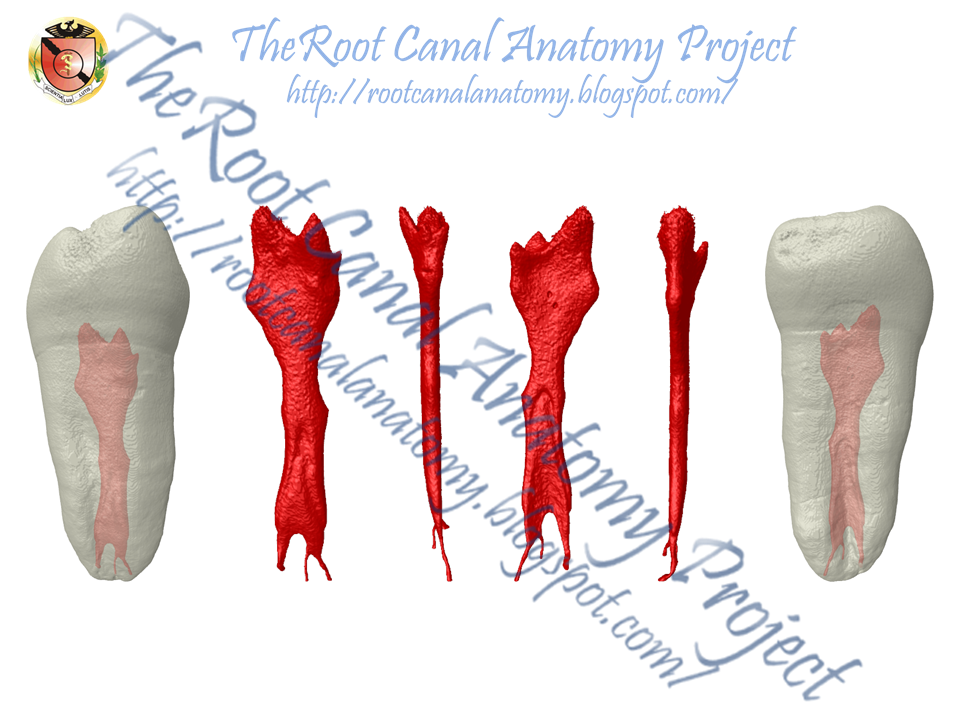
JOE Publication: Radix
Introduction: The morphology of the supernumerary third root (radix) in mandibular first molars was examined by micro–computed tomography (mCT) scanning.
Methods: Nineteen permanent mandibular first molars with radix were scanned in amCT device to evaluate their morphology with respect to root length, root curvature direction, location of radix, apical foramen, accessory canals and apical deltas, and distance between canal orifices as well as 2- and 3-dimensional parameters of the canals (number, area, roundness, major/minor diameter, volume, surface area, and structure model index). Quantitative data were analyzed by 1-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test (P<.05).
Results: The mean length of the mesial, distal, and radix roots was 20.36 ± 1.73 mm, 20.0 ± 1.83 mm, and 18.09 ± 1.68 mm, respectively. The radix was located distolingually (n= 16), mesiolingually (n= 1), and distobuccally (n= 2). In a proximal view, most radix roots had a severe curvature with buccal orientation and a buccally displaced apical foramen. The spatial configuration of the canal orifices on the pulp chamber floor was mostly in a trapezoidal shape. The radix root canal orifice was usually covered by a dentinal projection. The radix differed significantly from the mesial and distal roots for all evaluated 3-dimensional parameters (P< .05). The radix canal had a more circular shape in the apical third, and the mean size of the minor diameter 1 mm short of the foramen was 0.25 ± 0.10 mm.
Conclusions: The radix root is an important and challenging anatomic variation of mandibular first molars, which usually has a severe curvature with a predominantly distolingual location, and a narrow root canal with difficult access.
May 8, 2014
Bruker-MicroCT Meeting 2014 - Belgium
Prof. Dr. Marco Versiani - University of Sao Paulo, Brazil
5-8 May - Ostend / Belgium 2014
3D Mapping of the Irrigated Areas of the Root Canal Using Micro-CT
Prof. Dr. Graziela Bianchi Leoni - University of Sao Paulo, Brazil
5-8 May - Ostend / Belgium 2014
Push-out of root canal filling using the material testing stage (MTS)
inside a Micro-CT: preliminary observations
April 24, 2014
Publication JOE
Abstract
Introduction This study aimed to evaluate the frequency of dentinal microcracks observed after root canal preparation with 2 reciprocating and a conventional fullsequence rotary system using micro–computed tomographic analysis.
Methods Thirty mesial roots of mandibular molars presenting a type II Vertucci canal configuration were scanned at an isotropic resolution of 14.16 mm. The sample was randomly assigned to 3 experimental groups (n= 10) according to the system used for the root canal preparation: group A-Reciproc (VDW, Munich, Germany), group B-WaveOne (Dentsply Maillefer, Baillagues, Switzerland), and group C-BioRaCe (FKG Dentaire, La-Chaux-de-Fonds,Switzerland). Second and third scans were taken after the root canals were prepared with instruments sizes 25 and 40, respectively. Then, pre- and postoperative cross-section images of the roots (N= 65,340) were screened to identify the presence of dentinal defects.
Results Dentinal microcracks were observed in 8.72% (n= 5697), 11.01% (n= 7197), and 7.91% (n= 5169) of the cross-sections from groups A (Reciproc), B (WaveOne), and C (BioRaCe), respectively. All dentinal defects identified in the postoperative cross-sections were also observed in the corresponding preoperative images.
Conclusions No causal relationship between dentinal microcrack formation and canal preparation procedures with Reciproc, WaveOne, and BioRaCe systems was observed.
April 17, 2014
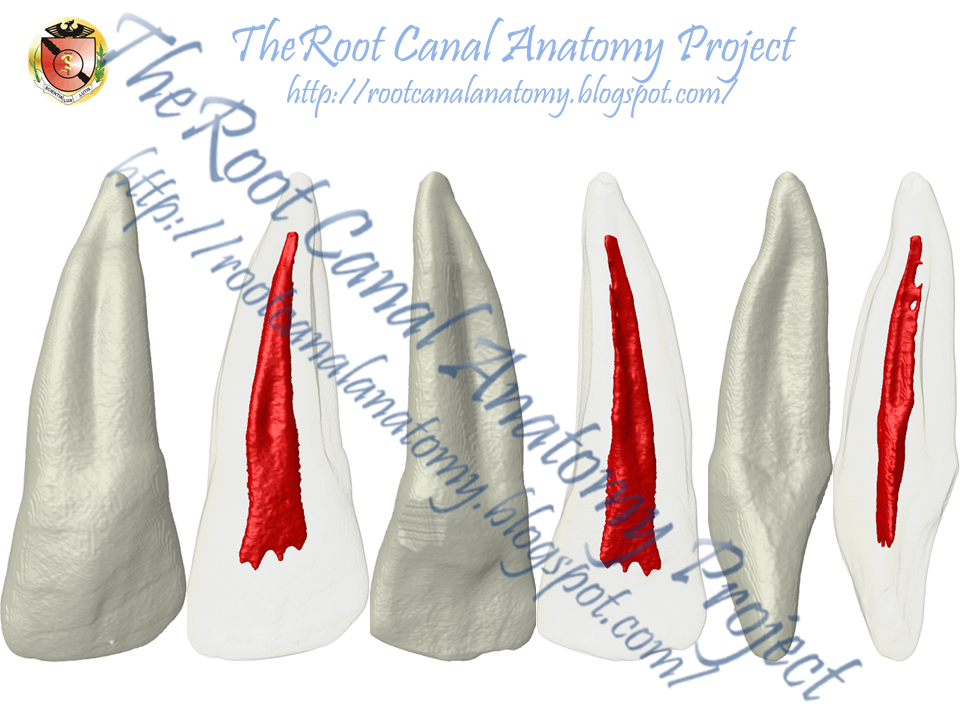
Radicular Groove: Maxillary Incisors
Radicular grooves (RGs) are a developmental groove in the root of teeth that may continue apically down the root. Grooves run from the beginning of the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ) and along the root surface to the apex. In most cases, the course of the grooves is straight.
Localization
Radicular grooves are often located on the palatal aspect of maxillary lateral incisors, and rarely on the labial root surface of the central incisors. RG were also reported in premolars and molars. According to their localization they are differentiated as distal, mesial and central patterns, with the distal position dominating, as it occurs in approximately 70% of cases. In the case of a distal localization, pathosis is often reported. The facial surface can be affected by the defect, albeit less frequently and with a predilection for the central maxillary incisors; however it is then properly termed a facial-radicular groove.
Localization
Radicular grooves are often located on the palatal aspect of maxillary lateral incisors, and rarely on the labial root surface of the central incisors. RG were also reported in premolars and molars. According to their localization they are differentiated as distal, mesial and central patterns, with the distal position dominating, as it occurs in approximately 70% of cases. In the case of a distal localization, pathosis is often reported. The facial surface can be affected by the defect, albeit less frequently and with a predilection for the central maxillary incisors; however it is then properly termed a facial-radicular groove.
Prevalence
The prevalence of PRGs ranges between 2% and 5%, with 58% of the grooves featuring a length of more than 5 mm.
Morphology
The grooves also vary in depth. Variation in groove depth can make a communication possible with the pulp cavity, however, deep grooves with direct communications with the pulp are seldom reported. With increasing depth of the groove, the thickness of the root cementum increases. At a morphological level, RGs are characterized by reduced dentin thickness and an increased cement layer, with a simultaneous modification of the odontoblasts. At a histological level, irregular dentin cement junctions have typically been identified.
Etiology
The etiology of RGs is unknown. Similar to an invagination, this seems to be a peculiarity of tooth development accompanied by a further anomaly. Black was the first to describe the RG as a malfor-mation during embryo development in 1908. Atkinson surmised that the reason for its formation is that there is not enough space during tooth development in the maxilla, resulting in folding in the area of the Hertwig epithelial sheath. In the opinion of Goon et, this could also be an attempt at a root partition. According to recent studies, RGs may be caused by genetic changes. The predominance of the palato-gingival groove in the maxillary lateral incisors suggests the possibility that the groove results from an undesirable position of the lateral incisor during the period of maxilla growth. The tooth, although still a germ, becomes surrounded by the central incisor, canine, and first premolar that are in a more advanced phase of dental development. Mineralization of the crown of the maxillary lateral incisor starts later, compared with the others, making this germ, under these conditions, highly susceptible to folding.
Clinical remarks
Morphological defects in dental structure (e.g. dens invaginatus, talon cusp, and the palato-gingival groove) can be predisposing factors for the onset of inflammatory processes in the periodontal and/or pulp tissues. The funnel-like shape of the palato-gingival groove promotes the accumulation of difficult-to-remove plaque and calculus, at times making proper cleaning by the patient, or even by the dentist, nearly impossible. Most of the time RGs are clinically overlooked so that recurring clinical symptoms are often misdiagnosed because of the pathogenesis. As there is no epithelial closure, it is possible for microbes to settle in the groove. Depending on the morphology of the RG, localized periodontitis may develop, accompanied by pathosis. Periodontal pocket depths of more than 5 mm and increased dental mobility are typical findings. Moreover, in the case of deep RGs, a retrograde pulpitis may occur as a result of the so-called endodontic-periodontal lesion.
Treatment
A good prognosis for prolonged tooth preservation also depends on whether combined periodontal and endodontic therapy is necessary. Several different procedures have been proposed for successful correction of RG. Current clinical treatment can correspond to that for inflammatory periodontal diseases. In some cases the palato-gingival groove can be seen in periapical radiographs as a fine parapulpal radiolucent line. In most cases, odontoplasty was carried out in combination with regenerative therapy. In the presence of periodontal disease, the therapeutical options can consist of grinding and flattening the affected area of the tooth with the groove, with the placement of a physical barrier between the tooth and soft tissue flap. The intraosseous defect, if present, can be grafted with porous hydroxyapatite. Other reported treatment procedures are careful root planing and cleaning, filling of the groove with amalgam or calcium sulphate, and intentional replantation after root planing and the insertion of Emdogain. The inherent difficulties in treating the palato-gingival groove make its diagnosis complex for practitioners. In some cases, the tooth was extracted due to its high mobility or in cases of bruxism.
Prognosis
The prognosis of pulp diseases and/or periapical inflammation in the presence of a palato-gingival groove is not very favorable, and depends in part on the groove’s extension, the depth of the groove, and the relation of the groove to the pulp cavity.
Sources
Arnold M.Palato-radicular groove associated with a bi-rooted maxillary incisor: a case report. Endo 2007;1:205-213.
Pécora JD, Conrado CA, Zuccolotto WG, et al.: Root canal therapy of an anomalous maxillary central incisor: a case report. Endod Dent Traumatol 1993; 9: 260-262.
Pécora JD, da Cruz Filho AM: Study of the incidence of radicular grooves in maxillary incisors. Braz Dent J 1992; 3: 11-16.
Pecora JD, Sousa Neto MD, Santos TC, et al.: In vitro study of the incidence of radicular grooves in maxillary incisors. Braz Dent J 1991; 2: 69-73.
Simon JH, Dogan H, Ceresa LM, et al.: The radicular groove: its potential clinical significance. J Endod 2000; 26: 295-298.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)